The plant Cannabis sativa is a puzzle made up of over 500 chemical substances, of which over 100 of them are considered “cannabinoids” (active components that can be used for medicinal, recreational, and synthetic purposes). In total, there are three main classifications of cannabinoids: phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids.
♦ Interested in high-quality CBD edibles and merchandise? Check out the FGE shop and FGE Etsy Store ♦
Phytocannabinoids, to put it simply, are plant-created cannabinoids that classify cannabis’s compounds. Examples include CBD and THC.
Endocannabinoids are the biological system that animals use to regulate food intake, glucose muscle metabolism, lipid synthesis in the liver, and many more essential tasks to get a body to live. Moreover, these are lipid-based neurotransmitters, further classified as CB1 and CB2.
Synthetic cannabinoids, as one may guess, are lab-made Cannabinoid look-alikes designed to offer a more potent effect than phytocannabinoids can offer.
Puzzle #1: Cannabinoid Acids
Naturally, cannabinoid acids are used to create compounds, the most common form of cannabinoids for human use.
Cannabinoid acids include:
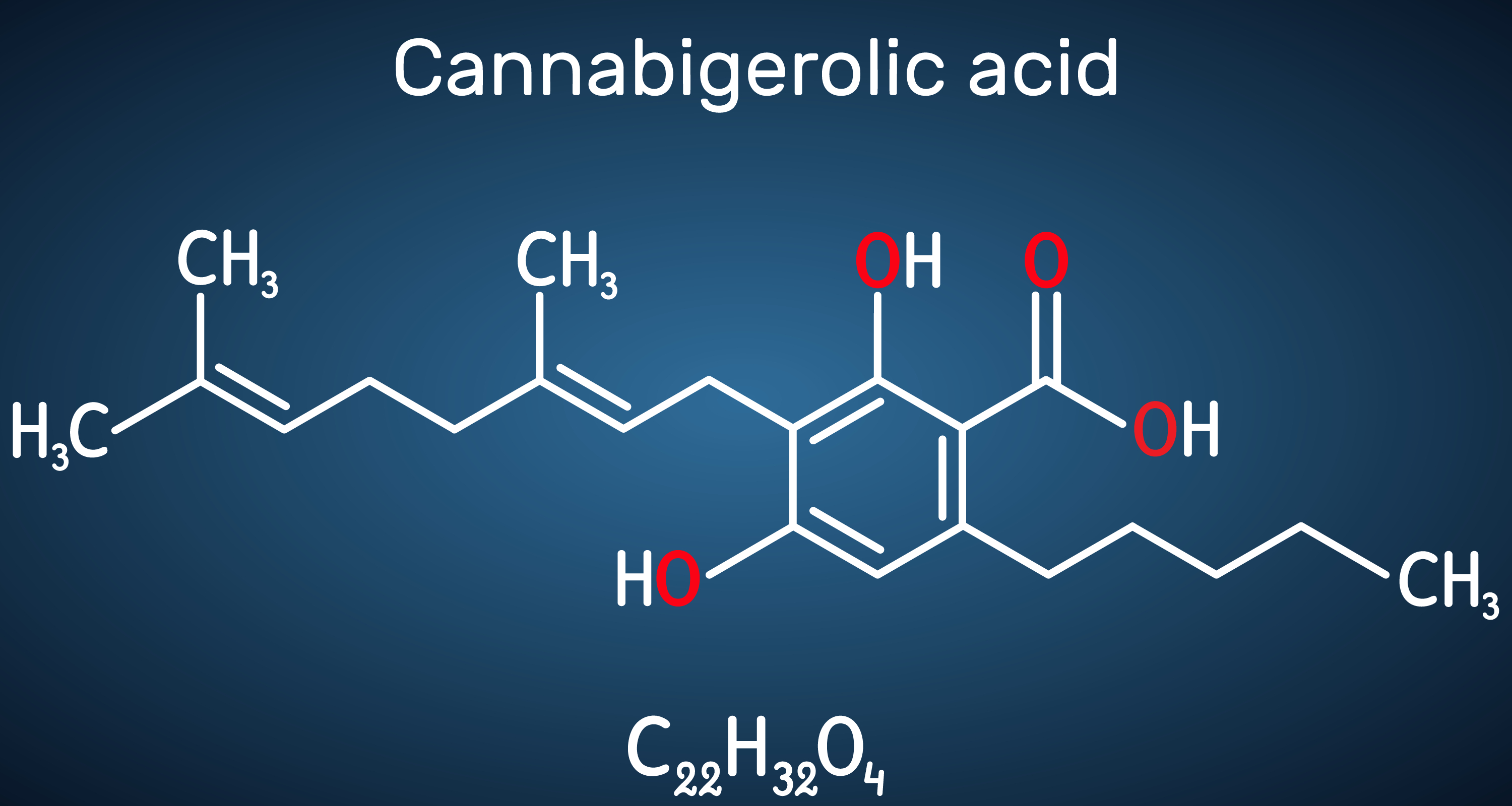
CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid)
Within the cannabis plant, CBGA is used to force resources into the cannabis plant flowers to ensure the maximum amount of plant energy. Considered to be one of the four main cannabinoids. This is the precursor of CBG.
THCA (Delta 9 tetrahydrocannabinol acid)
Considered to be one of the four main cannabinoids. Found within the leaves of a cannabis plant, THCA is the precursor of THC.
CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid)
Considered to be one of the four main cannabinoids. Most often found in the flowers of the cannabis plant, CBDA is the precursor of CBD.
CBCA (Cannabichromenenic acid)
Considered to be one of the four main cannabinoids, CBCA is the precursor of CBC.
CBGVA (Cannabigerovarinic acid)
CBGVA also has divarinolic acid, making it yet another precursor to CBG.
THCVA (Tetrahydrocannabivarin acid)
Just like the above, THCVA has divarinolic acid, making it yet another precursor to THC.
CBDVA (Cannabidivarinic acid)
Additionally, with divarinolic acid, CBDVA is yet another precursor to CBD.
CBCVA (Cannabichromevarinic acid)
Finally, with divarinolic acid, CBCVA is yet another precursor to CBC.
Puzzle #2: Natural Cannabinoid Compounds
Cannabinoid compounds are created when most cannabinoid acids are “activated” through intensive heat. These are the most popular ways to deliver cannabinoids to the human system.
Cannabinoid compounds include:
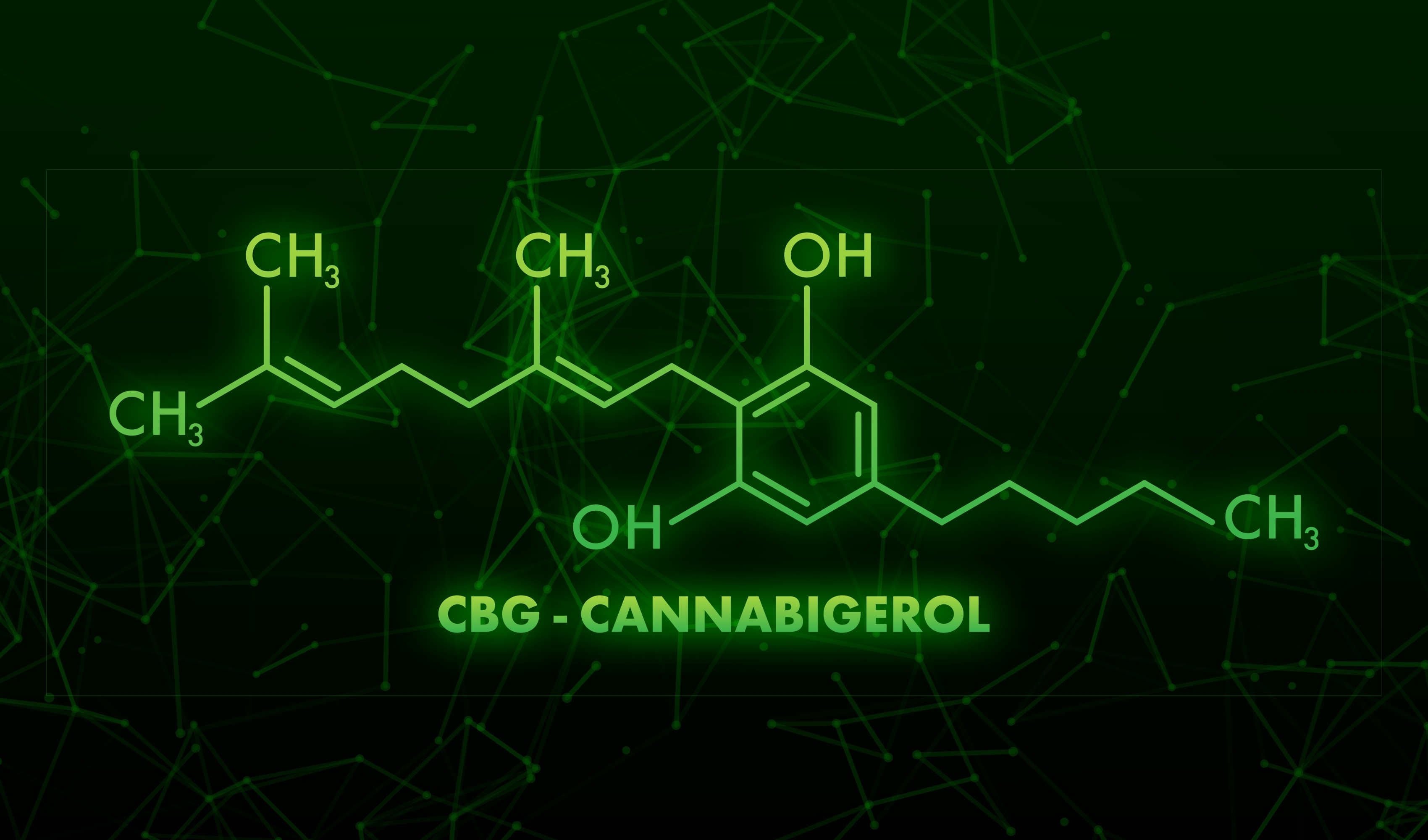
CBG (Cannabigerol)
Also known as the “mother of all cannabinoids,” because it’s the precursor to all other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC. It does not offer any kind of high.
CBG is most commonly used for relieving anxiety and stress.
∆9-THC (Delta 9 tetrahydrocannabinol)
This form of THC is the most potent, high-inducing natural version of THC. It is a psychoactive drug and should be taken under strict instructions to prevent any sort of overdose or negative bodily reaction.
∆8-THC (Delta 8 tetrahydrocannabinol)
Delta 8 THC is a less potent version of Delta 9 THC. Delta 8 gives a “high,” but it will be considerably less than its Delta 9 counterpart.
CBD (Cannabidiol)
The cannabinoid CBD is one of the most popular forms of cannabis due to its versatility and effects. CBD is THC’s non-psychoactive sibling, capable of easing pain and stress without any unwanted psychoactive effects. CBD has also been shown to calm epileptic episodes and seizures, earning itself an FDA-approved prescription label (the first of its kind).
There are three main types of CBD: full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate.
Full-spectrum is when the entire natural cannabis plant is used to create CBD. This form of CBD will have trace amounts of THC. 0.3% or less of THC is the legal amount in most countries.
Broad-spectrum is when only certain parts of the plant are used, which creates a product often free of THC. However, similar to full-spectrum, this category can contain trace amounts of THC.
Isolate is when the entire cannabis plant is extracted, leaving nothing but pure, completely THC-free CBD behind. This version is the safest kind of CBD that exists.
CBC (Cannabichromene)
Most often used as an anti-inflammatory, capable of relieving pain. This cannabinoid does not offer any sort of high.
CBN (Cannabinol)
CBN was the first cannabis compound to be isolated, all the way back in the 1800s. It is considered to be a “mildly psychoactive” drug, nearly 90% weaker than THC. Often, CBN is used as a sleep aid, even capable of relieving pain from chronic diseases such as Crohn’s disease and arthritis.
CBE (Cannabielsoin)
CBE is thought to be useful against epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and pain, but needs to undergo further research.
CBF (Cannabifuran)
Considered to be rare, this compound is so difficult to find naturally, that scientists must use heat to draw it out instead. The effects of CBD are rather unknown, and the purchase of this compound isn’t a simple walk to the convenience store. (Well, none of these cannabinoids are, but this one especially.)
CBL (Cannabicyclol)
Not much is known about this compound either, although it has been known to stimulate appetite, ease pain, and reduce nausea.
CBT (Cannabitriol)
First isolated in 1966, CBT is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid known best for its ability to assist in the management of glaucoma.
CBR (Cannabiripsol)
One of the newest compounds found within the cannabis plant. More research must be done to understand its full effects.
CBV (Cannabivarin)
A non-psychoactive cannabinoid great for mood disorders, neuropathic pain, and multiple sclerosis.
Puzzle #3 and Puzzle #4: Synthetic and Semi-Synthetic Cannabinoids
All synthetic cannabinoids are lab-created, human-made variations of natural cannabinoids, created most commonly through chemical synthesis and biological synthesis.
Synthetic cannabinoids include:
HU-210
A synthetic form of THC. It has a potency of nearly 100X that of natural THC.
∆7-THC (Delta 7 tetrahydrocannabinol)
A synthetic isomer of THC. Only slightly less potent than ∆9-THC.
Semi-synthetic cannabinoids are created through low-THC cannabis.
An example of semi-synthetic cannabinoids include:
HHC
One of the very first semi-synthetic cannabinoids was discovered. Similar to ∆8-THC.
The information provided within this blog is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as professional advice. We cannot guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of the content presented here. Any actions or decisions you make based on this information are at your own risk. We advise consulting with qualified professionals if you require personalized advice. The opinions expressed here do not necessarily represent the views of all contributors or the organization behind the blog. We are not responsible for any errors or omissions, nor for any damages resulting from your use of this blog. By using this blog, you agree to these terms.